Shared Filesystem
Shared filesystems in the 1.5.3 release are currently in Technology Preview. This experimental feature is not yet intended for production use.
Shared Filesystem support allows volumes to be mounted for read & write access
by multiple containers simultaneously, even from different nodes. In
Kubernetes, shared filesystems are referred to as ReadWriteMany or RWX
volumes.
Follow the Operations page to learn
how to deploy and use ReadWriteMany PersistentVolumeClaims (PVCs).
Architecture
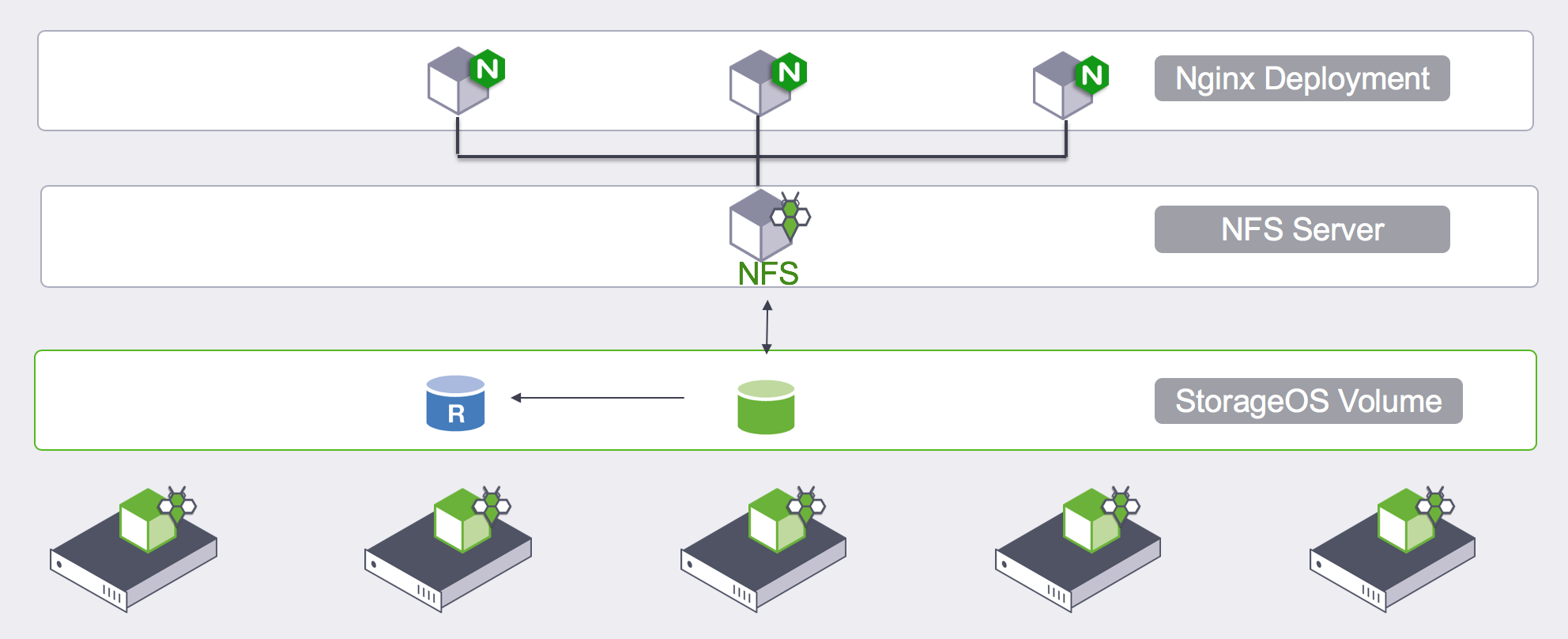
The default StorageOS StorageClass can create volumes with either
ReadWriteOnce (RWO) or ReadWriteMany (RWX)
AccessModes.
When requesting a RWX PVC, StorageOS will provision a standard RWO volume and mount the volume into an NFS server instance dedicated to this volume.
The NFS server is provisioned as a StatefulSet, which is created by the
StorageOS Cluster Operator using an NFSServer Custom Resource Definition. The
configuration of the NFS server is stored in a ConfigMap. The ConfigMap defines
the export location matching the RWO volume that StorageOS dynamically
provisioned to back the NFS server.
Separate Services are defined for the NFS traffic and for HTTP-based health and metrics traffic.
The NFS traffic Service is on port 2049 and uses TCP only to allow simple
exposure to clients outside the Kubernetes cluster. Clients must be capable of
NFS version 4.2 which has numerous (primarily performance) advantages over
previous revisions.
The StorageOS NFS server exposes a health endpoint on
http://<PodIP>:80/healthz.
HTTP 200/OKwill be returned when the server is operational and sending heartbeat messages.HTTP 503/Service Unavailablewill be returned if the server hasn’t sent a heartbeat message within 10 seconds.
Prometheus metrics for the NFS server, clients and IO activity are available on
http://<PodIP>:80/metrics.
Details of the StorageOS NFS Server implementation are available on Github.
The NFS server Pod and the RWO StorageOS volume are placed in the same Namespace as the RWX PVC.
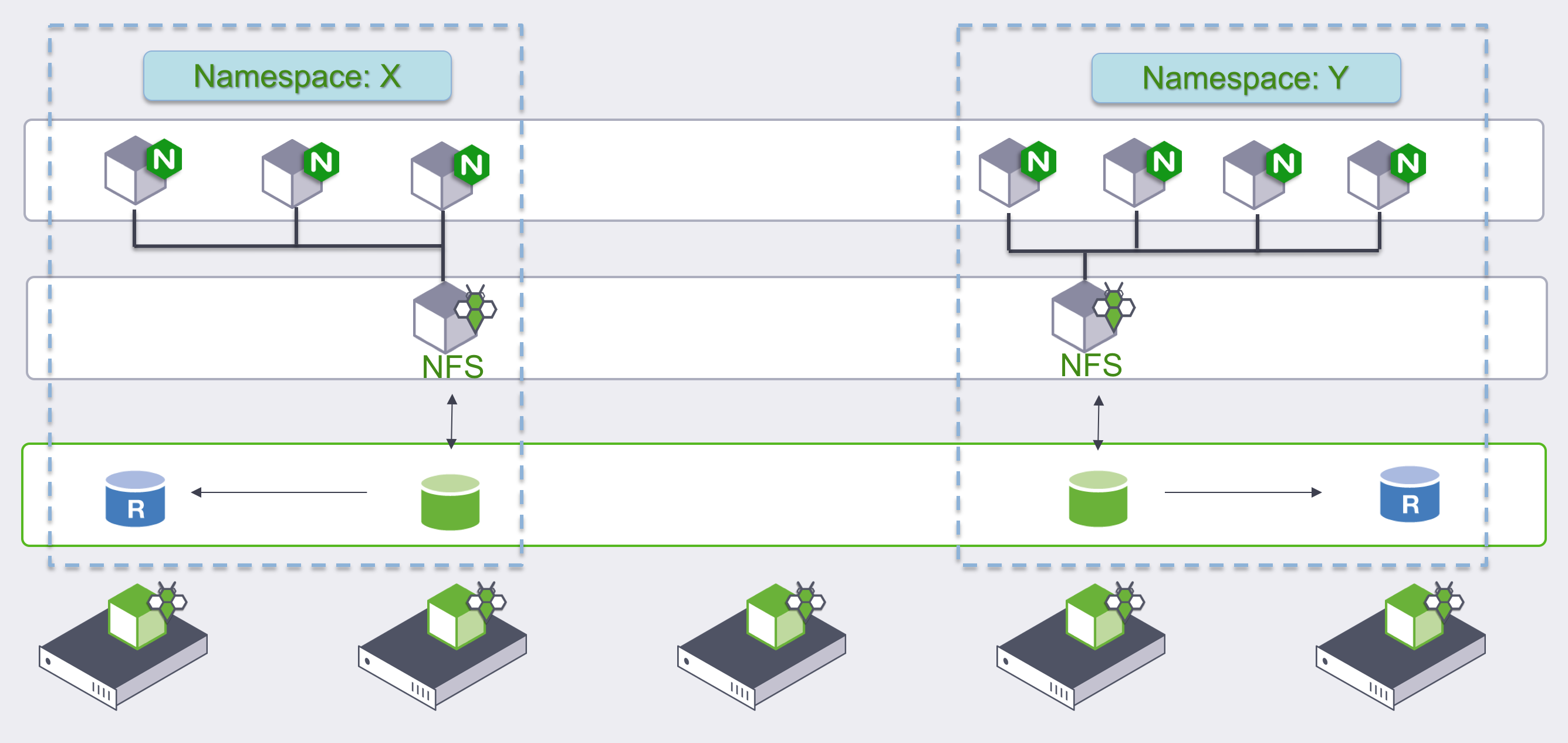
The NFS server StatefulSet is named after the RWO Persistent Volume.
Therefore the NFS Pod will be named in the form of pvc-${UID}-0.
Once the NFS server is healthy and sharing the RWO volume’s filesystem, the RWX volume is available for use. It takes slightly longer to provision a RWX volume for the first time as the NFS server image has to be pulled.
The StorageOS RWO backing volume will be updated with labels:
storageos.com/nfs.server: NFS server endpoint.storageos.com/nfs.share: NFS share path.
The RWX Volume is a Kubernetes construct backed by StorageOS Volumes, therefore the StorageOS API will not report on shared volumes.
Labels
StorageOS uses labels to apply behaviour regarding the Volumes. Feature labels can be passed to the RWX PVC to ensure that the underlying StorageOS volume backing the NFS server implements those features
For instance, to enable replication, set the label storageos.com/replicas: 1
in the RWX PVC metadata.
Fencing
StorageOS implements fencing for StatefulSet based pods. When replication has been enabled, the NFS server will use the fencing feature to ensure rapid failover when the node fails.
CSI
Shared Filesystems / RWX volumes are only supported by StorageOS when using CSI (Container Storage Interface).